
Video Subtitles: Types, Benefits & Useful Tips to Get You Started
Do you turn the sound off when you watch a video? If yes, you are not alone. Many people choose to watch muted videos for a variety of reasons, including a noisy environment or the absence of headsets. Therefore, it’s crucial to make your videos accessible to everyone by adding subtitles and captions.
If you’re still questioning yourself, “Why do I need subtitles?” this article is for you. Dive in to find out what video subtitles and captions are, their types, differences, benefits, and much, much more!
What Are Subtitles and Captions?
Captions are lines of text at the bottom of the screen that describe the audio content of a video for viewers who may not be able to hear it. Subtitles, on the other hand, are translations of the dialogue spoken in the video into another language, primarily for viewers who can hear but do not understand the language. Both are used to make content more accessible, including for viewers with hearing impairments.
Now that you know what is the purpose of a subtitle and caption, let’s move on to different types of subtitles and find out why are captions important.
Subtitle Types
Forced narrative (FN) subtitles, SDH (Subtitles for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing), and non-SDH are the three main types of subtitles. The type you select will greatly depend on the objective of your videos and the target audience. Let’s quickly define each type before we go into more detail.
FN
Forced narrative (FN) subtitles, often called forced subtitles, provide important information that viewers need to understand. These subtitles appear as overlay text to clarify dialogue, explain burned-in graphics, and provide other details that might not be clear to the audience.
SDH subtitles
SDH subtitles for videos are similar to closed captions in that they are also optional and usually appear at the bottom part of the screen. However, because they were written with a deaf or hard-of-hearing audience in mind, they will include other audible aspects to aid the audience in understanding the action or atmosphere of the scene. For instance, an SDH subtitle might feature phrases like “indistinct chatter” or “sad music plays.” This subtitle type is most frequently used in movies when the action rather than the dialogue is crucial.
Non-SDH
Non-SDH, or subtitles not meant for the deaf and hard of hearing, are usually just called “subtitles.” They are made for viewers who can hear but don’t understand the language. Non-SDH only include dialogue, but if there’s enough time, any on-screen graphics or words can also be included.
Open vs. Closed
Both subtitles and captions can be open and closed. Open captions are burned into the video and cannot be turned off, while closed captions can be toggled on or off and are often found in DVDs and streaming services. Closed captions typically appear at the bottom of the screen, offering viewers the flexibility to enable or disable them as needed.
Types of Closed Captioning
608
608 closed captions (also called EIA-608, CEA-608, or Line 21 captions) were the standard type of captions for analog TV. These captions can’t be changed by viewers, but they do work with digital TV.
708
708 closed captions (also known as EIA-708, CEA-708, or CTA-708 captions) are the updated standard for digital TV. These captions can be customized by viewers, but they don’t work with analog TV.
Captioning vs Subtitles
Although the terms subtitles and captions are sometimes used synonymously, significant distinctions exist between them.
The difference between closed captions and subtitles is as follows:
Closed captions
- Captions provide a textual representation of the audio content in its original language.
- Captions are used to transcribe what is being said in a video, program, or movie.
- Captions also provide additional audio cues for sound effects and background music.
- Captions help deaf people and people who are hard of hearing understand spoken words and other audio information.
Subtitles
- Subtitles are textual translations of a video’s dialogue.
- Subtitles are shown to the international audience, including people with hearing impairments, in their native language to aid comprehension.
- Subtitles can include additional audio cues as to the sound effects and background music (in the case of SDH subtitles).
- Subtitles in many languages can be seen on streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, Apple TV, etc.
Here’s a good example:
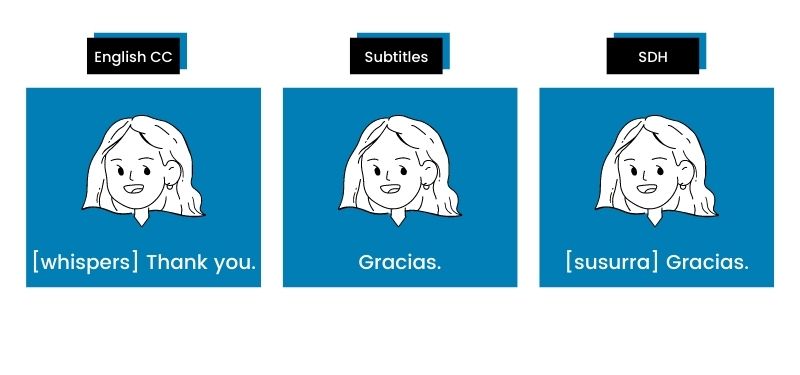
Not confident about your captioning or subtitling skills? Don’t worry — you can always hand the task over to professional typing services and save time and stress.
Benefits of Subtitles & Captions
Apart from helping people with hearing impairments and foreigners understand and enjoy the content, subtitles and captions are also important for a number of reasons. These include the following:
- Captions and subtitles help people studying a foreign language recall and understand the material and develop listening skills through exposure to authentic use of language.
- Captions and subtitles help people watching videos in noisy environments clearly understand the video, even when the sound is turned off.
- Captions and subtitles improve engagement and viewing time by making video content accessible to all categories of viewers.
- Captions and subtitles make videos more searchable, helping their creators reach a wider audience.
- Captions and subtitles help understand muddled audio tracks and difficult accents.
- Captions and subtitles help videos rank higher in SERPs.
- Captions and subtitles help people watching videos at different speeds catch all critical information.
- Captions and subtitles provide context for the visuals so that viewers can follow the action when the audio is difficult to understand.
- Captions and subtitles make it easier for clients looking for your services on search engines like Google to find your business.
The cognitive benefits of reading subtitles are also hard to underestimate, as they strengthen reading skills, boost comprehension and attention to detail, and improve memory.
While the advantages of using subtitles and captions are clear, many people still mix up these terms. Let’s explore why that confusion arises.
Why Are Captions and Subtitles Often Mixed Up?
Captions and subtitles are often confused with each other, and there are several reasons why. Let’s find out how differences in global terminology and the increased use SDH have contributed to the confusion.
Global Terminology Differences
In many countries outside the U.S. and Canada, such as the UK and Ireland, captions and subtitles are considered the same thing. The term “subtitling” is used for both translating foreign languages and helping deaf or hard-of-hearing viewers.
With video content being shared globally, people often mix up “captions” and “subtitles,” especially when different regions use different terms.
Closed Captions vs Subtitles (SDH)
As video content spreads worldwide, closed captions (CC) and Subtitles for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (SDH) are frequently mistaken for one another. They may look similar, and both serve deaf and hard-of-hearing viewers, but they are different.
What Are Subtitles in a Text?
SDH were originally created to help viewers who can’t hear or understand the language. But many platforms now use SDH in place of traditional captions. Some platforms label these as “SDH,” others call them “CC,” and sometimes both.
What Is the Difference Between Subtitles and Captions?
While both improve video accessibility for viewers, the difference between captioning and subtitling is complex, and they can’t be easily compared in simple terms. Captions provide a text representation of the audio in its original language, including sound effects and background music cues. They are primarily aimed at deaf and hard-of-hearing viewers. Subtitles offer translations of dialogue for non-native speakers. They may also include audio cues in SDH formats but are mainly focused on dialogue comprehension for hearing viewers.
Understanding the details behind each is key to knowing how they differ. Here’s a quick look at each type:
|
Features |
Subtitles |
Captions |
|||
|
SDH |
non-SDH |
FN |
608 |
708 |
|
|
Audience |
Deaf and hard of hearing |
Hearing |
Hearing |
Deaf and hard of hearing |
Deaf and hard of hearing |
|
Transcription |
+ |
Just dialogue |
Only dialogue and information that may be difficult for the viewer to understand |
+ |
+ |
|
Text synchronized with the timing of the video |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Can be turned off |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
Used in source language |
+ |
At times |
At times |
+ |
+ |
|
Identification of a speaker |
+ |
– |
– |
+ |
+ |
|
Signs and graphics |
– |
At times |
+ |
– |
– |
|
Music and sound effects |
+ |
– |
– |
+ |
+ |
|
Translation options |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Limited |
Limited |
|
Appearance |
Varies, with a maximum of 42 characters per line |
Varies, with a maximum of 42 characters per line |
Varies, with a maximum of 42 characters per line |
White text displayed in a black box, with a limit of 32 characters per line |
White text displayed in a black box, with a limit of 32 characters per line |
|
Placement |
Typically centered at the bottom but can move to the top or above the lower third graphics |
Typically centered at the bottom but can move to above the lower third graphics |
Typically centered at the bottom but can move to above the lower third graphics |
Typically centered at the bottom but can move to the top |
Typically centered at the bottom but can move to the top |
|
Customization |
+ |
+ |
+ |
– |
+ |
How to Use Subtitles Correctly?
If you are thinking about subtitling or captioning your video, here are some essential tips to get you started:
- Pick a font that’s simple to read. The ideal typefaces for captions and subtitles are often sans-serif fonts like Arial or Helvetica.
- Make sure the text is readable and large enough. The ideal font size is often 12 points.
- Use a high-contrast text color, such as white on a dark background. This allows for easier reading.
- Use appropriate punctuation and grammar. This will make it simpler for people to understand your video.
- Ensure your captions and subtitles are to the point and two lines at most. Having fewer words to read on the screen would be appreciated by viewers.
- Place your subtitles and captions in a suitable location on the screen. The ideal position is the lower bottom third of the screen.
- Make sure your subtitles and captions appear precisely when the words are spoken. However, keep the text visible on the screen for 3 to 7 seconds.
- Always start sentences with capital letters and use lower and uppercase letters, not all caps.
- Set the minimum display time to 1.5 seconds in case of super short dialogue.
- No matter what language, slang, or dialect is used, ensure all actual words are written correctly.
- Always identify multiple speakers by their names.
- Caption quotes from famous people word-for-word.
Following these tips, you can make your captions and subtitles understandable and simple to read, improving accessibility for persons with hearing impairments and making it easier for viewers to follow your video.
How to Get Subtitles for a Video?
Different content platforms have varied requirements for captions and subtitles, making adding subtitles to your video material a real headache, especially if you haven’t done this before. Even worse, in some cases, those requirements constitute federal law. This means that before adding subtitles to your video, it’s crucial to do in-depth research on how to do so in your jurisdiction and hope the data you’ve found is accurate and up-to-date.
Alternatively, you can save the hassle and opt for professional video transcription services like typingservice.org. Our dedicated team of certified transcribers offers fully editable open/closed captions for videos and can format your subtitle translation fast and at an affordable price, delivering a 100% accurate, ready-to-use file that matches your requirements and industry standards.
We deal with all popular file formats and accept orders 24/7, so get started by uploading your video along with individual preferences here. You’ll be 100% satisfied, guaranteed!


